GNU tool-chain for MO_CPU2 68376
This CD contains GNU archives with development tools
targeted to Motorola m683xx processors, specially for MO_CPU1/2
mc68376 based board. Binaries of compilers are prepared for recent
GNU/Linux glibc-2 based host systems and for Windows
MinGW32
and Gygwin unix-like environment.
Tools Sources Sites
- GCC - GNU Compiler Collection
- http://gcc.gnu.org/
http://www.uclinux.org/pub/uClinux/m68k-elf-tools/gcc-3/
- Binutils - Assembler, Linker etc.
- http://sources.redhat.com/binutils/
- BDM Support for GDB - hardware assisted debugging
- http://sourceforge.net/projects/bdm/
http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~pisa/m683xx/bdm_driver.html
Linux archives
Archive of tools prepared for Linux Glibc-2
based systems
- m683xx-bdm-driver-040618.tar.gz
- mc683xx BDM interface Linux driver sources
need to be compiled for used host system
- bdm-load-030815.tar.gz
- m683xx BDM FLASH eraser and loader (Archive contains both static binary and sources)
- DDD - official site
- graphical front-end for plain GDB
- gcc-m68k-coff-3.4.3-bin.tar.gz
- m68k-coff GNU tool-chain includes GCC-3.4.3,
binutils, plain GDB with BDM support
C libraries for system-less setup
- gcc-m68k-elf-3.4.3-bin.tar.gz
- m68k-elf GCC 3.4.3 toolchain
- seyon-2.20c.tar.gz
- simple X based terminal for modems
and serial lines
- seyon68-cfg.tar.gz
- example invocation script and configuration
for terminal for /dev/ttyS1 = COM2 interface.
The subdirectory "src" contains sources user for building
of developmen toochains binaries.
Provided binutils are compiled with shared BFD library and are able
to disassemble and work with many different processors object formats.
Running of "ldconfig" is required after installation of
- /usr/lib/libbfd-2.15.so
- /usr/lib/libopcodes-2.15.so
shared libraries.
More informations about m68k, m683xx and ColdFire tools can be found at next sites:
- m68k elf tools for uClinux
- These tools are based on old GCC-2.95.3 compiller
- New m68k elf tools for uClinux
- These tools are result of heroic work of Bernardo Innocenti and are based on
recent GCC-3.3.x sources. The changes has been integrated into official GCC-3.4 distribution and our
tool-chain is upgraded to this version now.
- Pages with Pavel Pisa's branch of BDM patches for GDB
- The debugging tools provides driver
and reguired GDB-5.3 patches.
- Motorola m683xx and ColdFire BDM support development page
- This is place of joint forces to provide BDM support for GDB. Generic Chris Johns branch
for m683xx and ColFire CPUs. This branch can be used for building of tools for Windows
environment as well. Latest m683xx branch sources are in the SourceForge CVS as well.
Windows archives
There exist two environments trying to provide reasonable standard compliant environment
for GNU tools under Windows operating system.
- CygWin
- This environment tries to achieve compatibility with POSIX standard by providing
its own C runtime library (cygwin.dll) which emulates POSIX system-calls
as fork, link, unlink, etc.
- MinGW
- MinGW project is not aimed for full POSIX compliance. It tries use features
provided by Microsoft system runtime libraries.
CygWin environment and m68k toolchain
Installation of minimal set of CygWin packages is required to prepare
environment for cross-compiler tool-chain. Please, use CygWin site
to install base environment. The initial intention to provide snapshot of
live CygWin systems showed to be difficult, because installation phase
is required to correctly populate configuration.
The archives of development tools for CygWin environment are stored
in the directory m68k/tools/cygwin.
- GiveIO.zip
- Generic driver which enables acces to IO ports for Windows programs,
this driver is used by BDM tools for fast direct printer port manipulation.
Driver GiveIO.sys should be copyed into Windows system32/drivers
and registered by instdrv.exe.
- insdrv.exe
- Program to register driver without reboot.
usage instdrv.exe giveio c:\winnt\system32\drivers\giveio.sys
- giveio.reg
- Content of HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\giveio
registry branch after successful GiveIO installation. It can be even imported
and then instdrv.exe need not be used. One or two reboots should be enough.
If there is problem, deletion and recreation of registry branch should help.
- m68k-bdm-elf-gdb.exe
- CygWin binary of GDB-6.0 with BDM m683xx and ColdFire support.
- bdmctrl.exe
- Tool for batch target manipulation through BDM interface. This tool enables
among other things writing application image into target FLASH memory.
More information can be read from README.bdmctrl.
Help for recognized commands is printed when invoked with -h switch.
Tool can be even used for fast target assisted FLASHing mode, when target
FLASH program algorithm plugin is compiled.
- m68k-coff-binutils-2.15.96-cygwin-1.tar.gz
- Binary utilities (assembler, linker, etc) for m68k-coff target. Archive should be
extracted by tar -xzf m68k-coff-binutils-2.15.96-cygwin-1.tar.gz in the root
directory of CygWin instalation.
- m68k-coff-gcc-3.4.3-cygwin-1.tar.gz
- GCC-3.3.3 with NewLib C library for m68k-coff targets. Archive should be
extracted by tar -xzf m68k-coff-gcc-3.4.3-cygwin-1.tar.gz in the root
directory of CygWin instalation.
MinGW and MSYS m68k toolchain
All required packages should be found on the CD
in the directory archive/mingw.
- MinGW-3.1.0-1.exe
- Installation of MinGW libraries and native compiler tools.
- MSYS-1.0.10-rc-3.exe
- Archive of key individual packages available at the time of release.
- msysDTK-1.0.1.exe
- MSYS Developer Tool Kit.
- binutils-2.14.90-20040120-1.tar.gz
- Upgrade to latest native binary utilities for MinGW system.
Optional. required only for build of new cross-compilation tools
or native Windows application.
- gcc-core-3.3.1-20030804-1.tar.gz
- Upgrade to GCC-3.3.1. Optional. required only for build of new cross-compilation tools
or native Windows application.
- gcc-g++-3.3.1-20030804-1.tar.gz
- GCC-3.3.1 C++ language support. Optional. required only for build of new cross-compilation tools
or native Windows application.
The archives of development tools for MinGW environment are stored
in the directory archive/mingw/tools.
- GiveIO.zip
- Generic driver which enables acces to IO ports for Windows programs,
this driver is used by BDM tools for fast direct printer port manipulation.
Driver GiveIO.sys should be copyed into Windows system32/drivers
and registered by instdrv.exe.
- insdrv.exe
- Program to register driver without reboot.
usage instdrv.exe giveio c:\winnt\system32\drivers\giveio.sys
- giveio.reg
- Content of HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\giveio
registry branch after successful GiveIO installation. It can be even imported
and then instdrv.exe need not be used. One or reboot should be enough.
If there is problem, deletion and recreation of registry branch should help.
- m68k-bdm-elf-gdb.exe
- MinGW binary of GDB-6.0 with BDM m683xx and ColdFire support.
- bdmctrl.exe
- Tool for batch target manipulation through BDM interface. This tool enables
among other things writing application image into target FLASH memory.
More information can be read from README.bdmctrl.
Help for recognized commands is printed when invoked with -h switch.
Tool can be even used for fast target assisted FLASHing mode, when target
FLASH program algorithm plugin is compiled.
- m68k-coff-binutils-2.14.zip
- Binary utilities (assembler, linker, etc) for m68k-coff target. Archive should be
extracted in the root directory of MinGW instalation.
- m68k-coff-gcc-3.3.3.zip
- GCC-3.3.3 with NewLib C library for m68k-coff targets. Archive should be
extracted in the root directory of MinGW instalation.
Dev-C++ - Windows IDE for GCC based tool-chains
Homepage of Dev-C++
- devcpp4980.exe
- Dev-C++ IDE version 4.9.8.7.
Setup of Dev-C++ for m68k cross-compilation is described in in one of next
paragraphs. There has been found problem with Dev-C++ invocation of
MinGW Make and GCC program invocation. There has not been found problems
with CygWin based cross-compilation tools invocation.
Simple example application for MO_CPU1/2 board
- simple-m68k.tar.gz
- Linux simple directory snapshot.
To rebuild call make clean ; make ; in the simple directory.
- simple-m68k.zip
- Build directory snapshot from MinGW environment.
To rebuild call make clean ; make ; from MinGW shell
prompt in the simple directory.
- simple-m68k.tar.gz
- Build directory snapshot from CygWin environment.
To rebuild call make clean ; make ; from CygWin shell
prompt in the simple directory.
- simple.dev
- Dev-C++ project file for Simple appliaction.
- devcpp.ini
- Dev-C++ configuartion file with m68k-coff compiler setup.
The configuration file is hold in c:\Documents and Settings\user\Local Settings\Application Data.
Setup of Dev-C++ for m68k cross-compilation is described in in one of next
paragraphs. There has been found problem with Dev-C++ invocation of
MinGW Make and GCC program. Dev-C++ works well with CygWin based
cross-compilation tools.
Setup of Linux cross-development environment for m683xx MO_CPU1/2 targets
Working installation of recent distribution GNU/Linux system
based on Glibc-2 (libc-6) libraries and root privileges are necessary.
Binaries of all needed packages are provided except binary of
the Linux kernel BDM driver, which must be unpacked and compiled
against Linux kernel headers matching and configured for current
running Linux kernel. Basic steps
cd /usr/src
tar -xzf m683xx-bdm-driver-040618.tar.gz
cd m683xx-bdm-driver-040618
make
make install
depmod -a
should install binary of the driver into right place.
Device nodes must be created by provided "./MAKEDEV" command
for static "/dev" tree. When "devfsd" is used, device nodes
are created on fly. Default driver compilation setup uses
Linux Parport layer to access priter port. If the driver is compilled
without parport support then
Printer driver should be unloaded by
/sbin/modprobe -r lp parport_pc parport
And driver can be loaded by
/sbin/modprobe bdm
That process can be automated as described in the driver associated
README or in detailed description in the bdm_driver.pdf
file. Making of symbolic link "bdm" in the "/dev" directory pointing
to used interface is expected in next examples
cd /dev
ln -s icd_bdm0 bdm
equivalent to managing of link for devfsd setup
"/dev/bdm" -> "/dev/m683xx-bdm/icd0".
Next step is to unpack gcc-m68k-coff-3.4.3-bin.tar.gz archive
in "/" directory or better in temporary directory and manual
move to "/". Check if some files are overwritten and make appropriate
backup of original files. Run "ldconfig" command
Provided sample application named simple should compile
by "make" command now.
Connect the MO_CPU1/2 board to computer by serial cable.
Install seyon-2.20c.tar.gz simple terminal, look at example
configuration in archive/linux/tools/seyon68-cfg.tar.gz archive, copy "seyon68"
somewhere on the path and copy initialization script into
".seyon" subdirectory in your home directory. Open terminal
for right device (/dev/ttyS0 = COM1, /dev/ttyS1 = COM2).
Connect board to power supply +5VDC/500mA.
Next banner should appear.
# SIMPLE v0.5 build Pi Mar 26 2002 21:44:27
# test mode enabled
# kl41_lcd_init : -1
# date : 2002-03-28 01:49:57
You can type "help" command to see sample "simple"
application accepted commands. Commands names in
uppercase letters are part of motion controller
set and requires character ":" for assignment of value and
character "?" for query. Other commands are simple command line
tests. "date" can be used for date/time read and when new
value in same format is appended, date is adjusted to that value.
Commands for flash tests can be applied only to that chip,
which is not used for instruction fetches (ie. "flashid 0x900000")
is OK, but (ie. "flashid 0x800000") is not, when code runs from FLASH.
Command "gdbbreak" can be used for establish of serial GDB stub debugging.
It takes one parameter - level :
- disable serial stub
- enable serial stub and redirect RS232 Ctrl+C to stub
- enable stub and initiate break immediately and wait for GDB
execution can be continued by
(gdb) p $pc=$pc+2
to skip breakpoint instruction
- - redirects all RS232 communication to the GDB stub
- - disables "simple" application interrupts and wait for GDB
to load new executable
Connection of BDM debugging interface.
Power board off.
Make sure, that logic ground of mc68376 microcontroller
is interconnected with PC chassis ground before plugging
BDM interface parallel port cable. Plugging of cable when
there is voltage differential between MO_CPU1/2 board
and PC parallel port can lead to damage of the chip.
When same ground and supply is used for RS232 interface
and the microcontroller core (no galvanic isolation),
interconnection of RS232 cable is enough for voltage
rejection and board grounding. Connect BDM interface cable.
Power board up.
Start command "m68k-coff-gdb" (or "gdb68" shortcut) in the directory
with the right debugger initialization file ".gdbinit68"
and "cpu32init" SIM initialization files. Bellow is session example
bash-2.05# gdb68
GNU gdb
...
This GDB was configured as "--host=i686-pc-linux-gnu --target=m68k-bdm-coff"
Now set breakpoint
(gdb)b main
Breakpoint 1 at 0x31d8: file simple.c, line 1443.
download and execute application image "simple"
(gdb) run
Starting program: /root/m683xx/simple/simple
Do you want to download '/root/m683xx/simple/simple'
(y or n) y
Both LEDs on BDM interface should lit for while.
Then should both switch-off and immediately freeze LED
should lit again as address of breakpoint is reached
Breakpoint 1, main () at simple.c:1443
1443 { unsigned flags=0;
(gdb)
(gdb)c
Continues application in full-speed and example commands
could be set through serial terminal.
Now you can use "Ctrl+c"
to stop and then "s", "c",
"p <variable>"
commands or you can install Insight or DDD front-ends from archives
ddd-3.3.1.tar.gz and
m68k-coff-insight.tar.gz.
Gdb macro "bdm_hw_init" defined in "run376.gdb" can be invoked at any time
to reset target when GDB debug session is run. Automatic reset and setup
of target before subsequent "run" commands can be requested by GDB command
"bdm_autoreset on". This command uses "cpu32init" in current directory
to setup SIM registers.
To place breakpoint into function "do_trap" could be useful for
exception catching in the "simple" application during development.
Both prepared versions of Linux GNU debugger (plain version
"gdb68" and TclTk version Insight "m68k-coff-insight") were
were tested with BDM interface (target bdm /dev/m683xx-bdm/icd0)
and serial (target remote /dev/ttyS1 equivalent to target remote COM2 for windows).
Serial stub of in the "simple" MO_CPU2 application can be invoked
by terminal command "bdmbreak'.
DDD fronted can be invoked for plain gdb (ddd68) as well.
Look to the directory "doc/bdm" for more informations about Linux
BDM debugging.
The full reference documentation for GNU debugger is placed in the directory
"doc/gnu/gdb".
There is runtime GDB "help" command as well.
Typing of "help bdm_" and pressing Tab key for completion lists all BDm subcommands.
Then help for each of them can be retrieved. The full BDM documentation is
BDM debbuging article.
CygWin
The delivered MO_CPU1/2 boards are tested and then simple application is written
into FLASH memory. When board is powered, it sends startup message
message to the RS-232 port and then receives simple commands.
The communication speed is set to 9600 Bd without parity and with one stop-bit.
This way correctness and functionality of RS-232 interconnection can be checked.
Next step is to interconnect BDM interface with target board
and PC computer printer port (LPT1).
Make sure, that logic ground of mc68376 microcontroller
is interconnected with PC chassis ground before plugging
BDM interface parallel port cable. Plugging of cable when
there is voltage differential between MO_CPU1/2 board
and PC parallel port can lead to damage of the chip.
An example of the cross-compiled project can be found in "/m683xx"
directory. There is "simple" application as
template for MO_CPU2 development. Commands to compile
make clean
make
make flash
generates RAM image "simple"
and FLASH image "flash".
The directory "boot" contains
board setup boot block "mo_flashbb".
Built application can be downloaded and run in target by GDB command line debugger.
m68k-bdm-elf-gdb
Windows version of GDB loads initialization script .gdbinit and access
printer port at address 0x378 when target bdm /dev/bdmicd0 is selected.
Same commands as for Linux GDB environment can be used.
Application can be load into RAM even by batch utility bdmctrl.
This way is even defined as Makefile target
make ram-load
Next procedure is used to download application image into FLASH memory.
make flash-burn
This erases FLASH memory and writes linked flash image
into FLASH memory. The example uses only slow host write method. Target assisted flashing
can be prepared for larger applications.
A linker scripts are used to define RAM and FLASH memory regions.
- mo_cpu1-1005.ld-cfg
- MO_CPU1/2 populated with 1MB RAM, 0.5MB FLASH
- mo_cpu1-1010.ld-cfg
- MO_CPU1/2 populated with 1MB RAM, 1MB FLASH
- mo_cpu1-2020.ld-cfg
- MO_CPU1/2 populated with 2MB RAM, 2MB FLASH
- mo_cpu1.ld-cfg
- Actually selected configuration included by other scripts
- mo_cpu1.ld-ram
- Memory layout for linking of application into RAM region
- mo_cpu1.ld-flash
- Memory layout for linking of application text and data initialization values
into FLASH. Space for read/write data and BSS is allocated in RAM region
- mo_cpu1.ld-boot
- Setup for building board initialization code stored FLASH boot block
Dev-C++ use with CygWin m68k tools
New compiller settings needs to be defined for use of Dev-C++ for cross development.
Tools -> Compiler Options is used to define new compiller set.
Cannonical target name m68k-coff is used in the example.
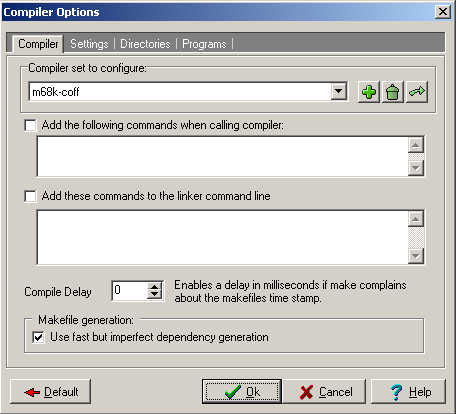
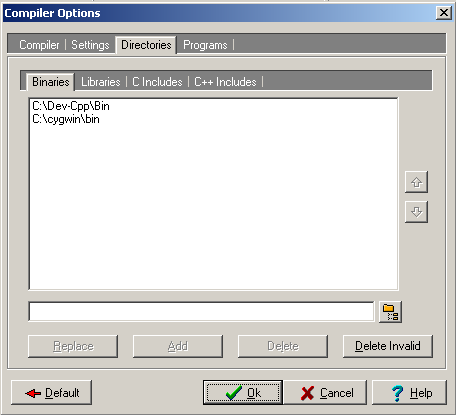
The CygWin binary directory has to be added to the binaries paths listing.
Command names of cross-compiller utilities used for target has to be defined.
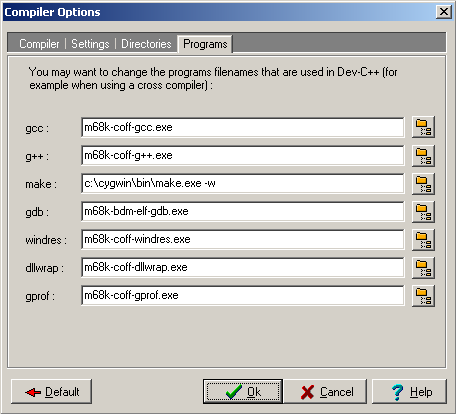
These options are held in c:\Documents and Settings\user\Local Settings\Application Data
directory. Configuration with m68k-coff target defined can be found in the provided file
devcpp.ini.
The project of target application has to specify name and set of used tools.
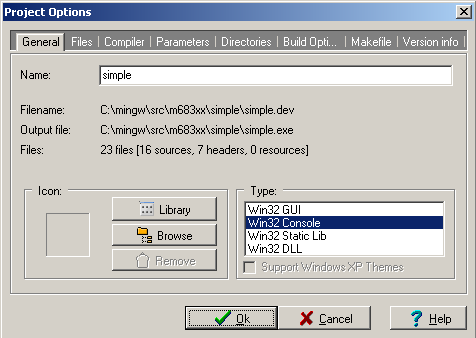
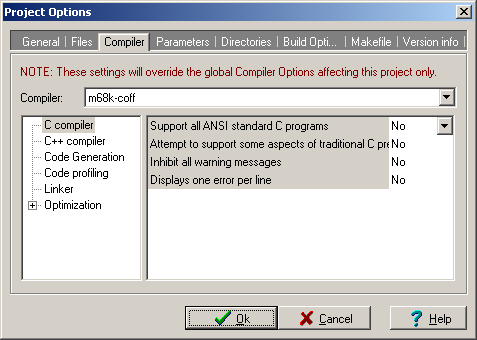
Some additional sub-architecture selecting options should be specified.
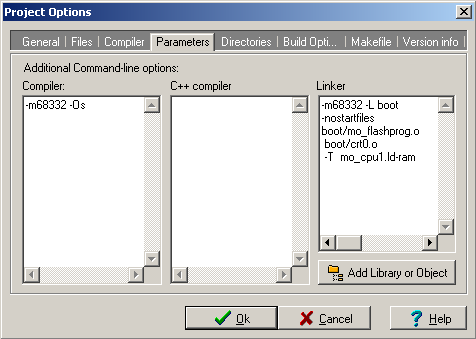
The linker script selection is mandatory to generate image for correct
memory region.
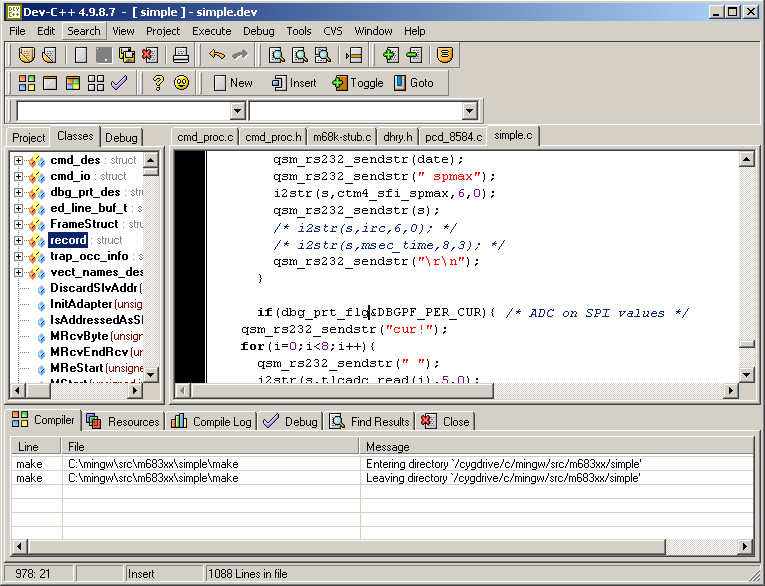
The example of project file for simple application can be found in
ther file simple.dev.
More documentation
Documentation is distributed between local copies and online references.
- Linux BDM debugging
- Article about BDM debugging
- Datasheets
- Datasheets for the components used on the MO_CPU2 board
- HTML documentation for GNU tools
-
- NEWLIB C Library
-
- MO_CPU2/MO_CPU2
-
Drawings for the second revision of the board
- PiKRON WWW pages
Disclaimer
All software and documentation is provided in hope to be useful,
but there is not WARRANTY of any kind.
All GNU software is freely distributable when contitions written in COPYING
file are met. We hope, that we have met all requirements by providing sources and configuration examples
of used software.
Example "simple" and m68k serial GDB stubs are provided without copyright restrictions
for use as template for real world embedded applications.
RTEMS copyright should be suitable for embedded applications as well.
This CD-ROM can be copyed freely .






